A) subsidy of more than $2.00 per tonne of rubber.
B) subsidy of $2.00 per tonne of rubber.
C) tax of more than $2.00 per tonne of rubber.
D) tax of $2.00 per tonne of rubber.
E) voucher valued at $2.10 a tonne of rubber.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider some type of industrial pollution that generates air pollution.This industry,if left unregulated,produces
A) more than the efficient level because producers ignore the marginal external costs.
B) the efficient level of output.
C) less than the efficient level because producers ignore the marginal external costs.
D) less than the efficient level because producers ignore the marginal external benefits.
E) more than the efficient level because producers ignore the marginal external benefits.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions. 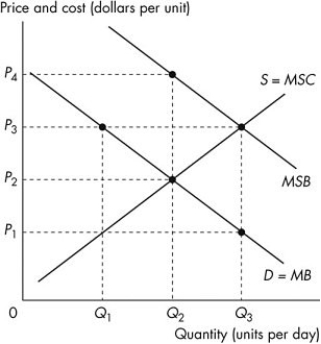 Figure 15.3.1
-Refer to Figure 15.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve,the marginal social benefit curve,and the market supply curve.If production is left to the private market,then the quantity produced is
Figure 15.3.1
-Refer to Figure 15.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve,the marginal social benefit curve,and the market supply curve.If production is left to the private market,then the quantity produced is
A) zero.
B) Q1.
C) Q2.
D) Q3.
E) between 0 and Q1.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the statement that is incorrect.
A) Between 2008 and 2012,carbon emissions in British Columbia remained constant.
B) As of 2012,British Columbia applies a carbon tax of $30 per tonne of carbon emitted.
C) British Columbia's carbon tax is revenue-neutral.
D) Ireland has a carbon tax.
E) A high gas tax in the United Kingdom cuts carbon emissions by inducing people to drive smaller cars and to drive less.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions. 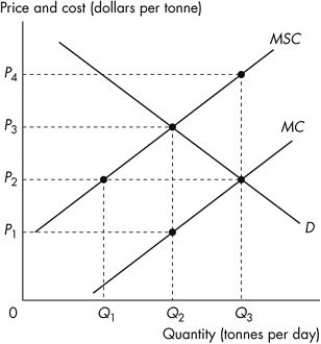 Figure 15.2.1
-Refer to Figure 15.2.1.The figure shows the marginal private cost curve,the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve of a mining firm.If the market is unregulated,then the price is
Figure 15.2.1
-Refer to Figure 15.2.1.The figure shows the marginal private cost curve,the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve of a mining firm.If the market is unregulated,then the price is
A) P1.
B) P4.
C) below P1.
D) P2.
E) P3.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Betty and Anna work at the same office in Calgary.They both must attend a meeting in Edmonton,and they have decided to drive to the meeting together.Betty is a cigarette smoker and her marginal benefit from smoking one package of cigarettes a day is $40.Cigarettes are $6 a pack.Anna dislikes cigarette smoke and her marginal benefit from a smoke-free environment is $50 a day.If Betty drives her car with Anna as a passenger,________.If Anna drives her car with Betty as a passenger,________.
A) Anna will offer Betty an amount between $34 and $50 and Betty will not smoke;Betty does not smoke because Betty will not offer Anna a high enough price to be allowed to smoke.
B) Betty will smoke because she owns the property rights in the car;Betty does not smoke because Betty will not offer Anna a high enough price to be allowed to smoke.
C) Betty will smoke because she owns the property rights in the car;Betty will offer Anna $51 and Betty will smoke.
D) Anna will offer Betty an amount between $34 and $50 and Betty will not smoke;Betty will offer Anna $51 and Betty will smoke.
E) Betty will smoke because she is the car owner;Betty will offer Anna an amount between $34 and $50 and Betty will smoke.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A market economy tends to ________ goods with negative externalities and ________ goods with positive externalities.
A) overproduce;overproduce
B) overproduce;underproduce
C) underproduce;overproduce
D) underproduce;underproduce
E) produce;consume
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions. 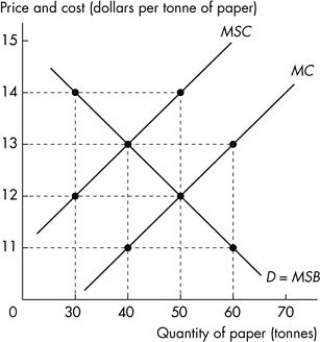 Figure 15.2.3
-Refer to Figure 15.2.3.A tax of ________ per tonne is necessary to achieve the efficient output of ________ tonnes of paper.
Figure 15.2.3
-Refer to Figure 15.2.3.A tax of ________ per tonne is necessary to achieve the efficient output of ________ tonnes of paper.
A) $14;50
B) $14;30
C) $13;40
D) $2;50
E) $2;40
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 15.2.2
Chemical Fertilizer Market 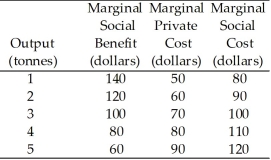 -Refer to Table 15.2.2.If the fertilizer market is perfectly competitive and unregulated,output is
-Refer to Table 15.2.2.If the fertilizer market is perfectly competitive and unregulated,output is
A) 1 tonne.
B) 2 tonnes.
C) 3 tonnes.
D) 4 tonnes.
E) 5 tonnes.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 15.2.1 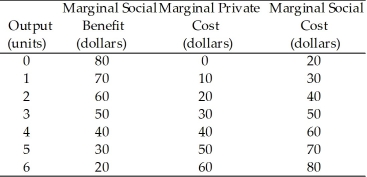 -Refer to Table 15.2.1.Given in the table are the marginal private cost and the marginal social cost of the production of chemical fertilizer and the marginal social benefit from the consumption of fertilizer.The table illustrates that this market has
-Refer to Table 15.2.1.Given in the table are the marginal private cost and the marginal social cost of the production of chemical fertilizer and the marginal social benefit from the consumption of fertilizer.The table illustrates that this market has
A) positive externalities,equal to $10 per unit.
B) negative externalities,equal to $10 per unit.
C) no externalities.
D) positive externalities,equal to $20 per unit.
E) negative externalities,equal to $20 per unit.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.  Figure 15.3.1
-Refer to Figure 15.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve,the marginal social benefit curve,and the market supply curve.If production is left to the private market,then the price is
Figure 15.3.1
-Refer to Figure 15.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve,the marginal social benefit curve,and the market supply curve.If production is left to the private market,then the price is
A) P1.
B) P3.
C) P2.
D) greater than P4.
E) P4.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.  Figure 15.2.1
-Refer to Figure 15.2.1.The figure shows the marginal private cost curve,the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve of a mining firm.If the market is unregulated,then the quantity produced is
Figure 15.2.1
-Refer to Figure 15.2.1.The figure shows the marginal private cost curve,the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve of a mining firm.If the market is unregulated,then the quantity produced is
A) zero.
B) Q1.
C) Q2.
D) Q3.
E) between Q2 and Q3.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Governments use subsidies
A) as a means of increasing government spending.
B) when they want to increase taxes.
C) to achieve an efficient outcome in a market with external costs.
D) to achieve an efficient outcome in a market with external benefits.
E) and pollution permits to achieve an efficient outcome in markets with external benefits.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way to solve negative externality problems is
A) to organize a limited boycott of the products.
B) subsidize the externalities.
C) eliminate transactions costs when property rights are not legally established.
D) issue pollution permits to polluting firms and establish a system of cap-and-trade.
E) establish and enforce patents and copyrights.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Coase theorem states that
A) patents and copyrights will solve the problem of external costs.
B) taxes will solve the problem of external costs.
C) global warming is hard to solve due to the prisoners' dilemma aspect of the problem.
D) property rights are social arrangements governing ownership,use and disposal of factors of production and goods and services.
E) if property rights exist,and the transactions costs of enforcing them are low,then private transactions are efficient and it doesn't matter who has the property rights..
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three ways governments can encourage production of goods with external benefits are
A) private subsidies,pollution permits,and intellectual property rights.
B) private subsidies,pollution permits,and vouchers.
C) intellectual property rights,pollution permits,and vouchers.
D) taxes,emission charges,and pollution permits.
E) private subsidies,vouchers,and intellectual property rights.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following illustrates the concept of a negative externality?
A) Bad weather reduces the size of the wheat crop.
B) A reduction in the size of the wheat crop causes income of wheat farmers to fall.
C) Smoking harms the health of the smoker.
D) Smoking harms the health of nearby nonsmokers.
E) Public health services reduce the transmission of disease.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following statements are correct except
A) knowledge about one process spills over into other segments of the economy.
B) additional knowledge makes people more productive,and there seems to be no tendency for the additional productivity from additional knowledge to diminish.
C) knowledge has no external benefit.
D) knowledge might be an exception to the principle of diminishing marginal benefit.
E) it is necessary to use public policies to ensure that those who develop new ideas have incentives to encourage an efficient level of effort.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The devices the government can use to achieve a more efficient allocation of resources in the presence of external benefits include all of the following except
A) intellectual property rights.
B) subsidies.
C) public production.
D) pollution permits.
E) patents.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions. 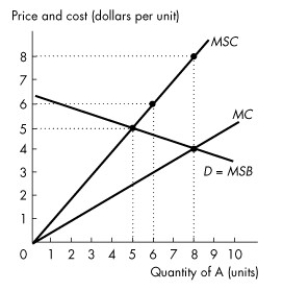 Figure 15.2.2
-Refer to Figure 15.2.2.This figure shows the demand curve,the marginal private cost curve and the marginal social cost curve of good A.What is the efficient quantity of good A?
Figure 15.2.2
-Refer to Figure 15.2.2.This figure shows the demand curve,the marginal private cost curve and the marginal social cost curve of good A.What is the efficient quantity of good A?
A) 0 units
B) 5 units
C) 6 units
D) 8 units
E) more than 8 units
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 114
Related Exams