A) generates many local potentials.
B) is insensitive to further stimulation.
C) responds to even weak stimuli.
D) reverses the direction of the action potential.
E) is very sensitive.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gray matter on the surface of the brain is/are called
A) the cortex.
B) nuclei.
C) ganglia.
D) tracts.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Gray matter consists of bundles of myelinated axons.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Saltatory conduction of an action potential means that
A) once one action potential is created,it moves down the axon.
B) the whole axon depolarizes at the same time.
C) one action potential stimulates the production of a new action potential at the adjacent site.
D) an action potential is conducted from one node of Ranvier to the next node.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Protein synthesis in neurons occurs in
A) axons.
B) dendrites.
C) cell bodies or soma.
D) terminal boutons.
E) node of Ranvier.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sensory neurons carrying action potentials from pain receptors synapse within the spinal cord with interneurons.These interneurons synapse with motor neurons leading back to an effector and ascending neurons that carry action potentials toward the brain.This is an example of a(n) _____ pathway.
A) convergent
B) divergent
C) reverberating
D) sensory
E) bifurcated
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sensory (afferent) division of the peripheral nervous system
A) transmits action potentials to sensory organs.
B) conveys action potentials to the CNS.
C) stimulates glands to release hormones.
D) stimulates muscle contractions.
E) does not involve sensory receptors.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Multiple sclerosis is a neurological disorder in which myelin sheaths in the CNS are destroyed.Which of the following neuroglial cells is being damaged in multiple sclerosis?
A) astrocyte
B) microglial cell
C) oligodendrocyte
D) ependymal cell
E) Schwann cells
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you cut bundles of axons and their myelin sheaths in the PNS,you cut
A) ganglia.
B) nuclei.
C) nerves.
D) gray matter.
E) nerve tracts.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
LouAnn is being treated for a neurological condition with a specific drug that target neurons deep within the brain.Which glial cell must be bypassed by this drug in order for it to be effective?
A) astrocyte
B) microglial cell
C) oligodendrocyte
D) ependymal cell
E) macrophage
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fran has a microbial infection attacking his brain.Which cell type would you expect to proliferate and be most active during this time?
A) astrocytes
B) microglial cells
C) oligodendrocytes
D) ependymal cells
E) Schwann cells
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The nervous system has two subdivisions - the central nervous system and the ____________ nervous system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The autonomic nervous system
A) stimulates skeletal muscle contractions.
B) has two sets of neurons in a series.
C) is involved in problem solving.
D) is under voluntary control.
E) does not include the central nervous system.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
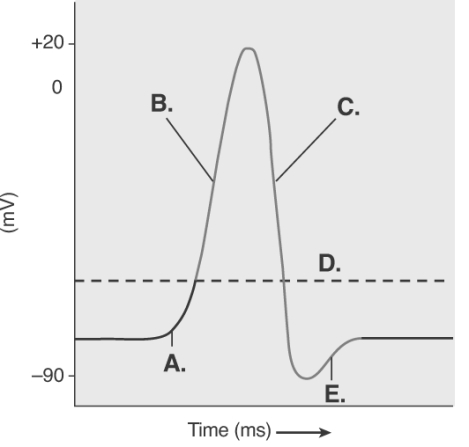 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "D" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "D" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is responsible for problem-solving skills?
A) central nervous system
B) peripheral nervous system
C) somatic nervous system
D) autonomic nervous system
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Schwann cells differ from oligodendrocytes in which of the following ways?
A) Schwann cells form myelin; oligodendrocytes do not.
B) Oligodendrocytes are only found in the PNS; Schwann cells are only found in the CNS.
C) Schwann cells form sheaths around several axons,while oligodendrocytes form sheaths around only one axon.
D) Schwann cells form a myelin sheath around a portion of only one axon,while oligodendrocytes can surround portions of several axons.
E) None of these choices are true differences.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nissl bodies are
A) part of a dendrite.
B) also called gemmules.
C) lipid droplets.
D) areas of rough endoplasmic reticulum.
E) part of the Golgi apparatus.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
White matter is composed of
A) ganglial sheaths.
B) bundles of myelinated axons.
C) collections of nerve cell bodies.
D) bundles containing both myelinated axons and nerve cell bodies.
E) collections of unmyelinated axons.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Most unipolar neurons are ____________ neurons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Digestion of food is regulated by the
A) sensory division.
B) sympathetic division of the ANS.
C) parasympathetic division of the ANS.
D) somatic nervous system.
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 155
Related Exams