A) the crowding-out effect.
B) the interest-rate effect.
C) investment demand curves.
D) money demand curves.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPS in an economy is .1, government could shift the aggregate demand curve rightward by $40 billion at each price level by:
A) increasing government spending by $4 billion.
B) increasing government spending by $40 billion.
C) decreasing taxes by $4 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $4 billion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A public debt which is owed to foreigners can be burdensome because:
A) foreign interest rates are persistently higher than domestic interest rates.
B) payment of interest reduces the volume of goods and services available for domestic uses.
C) payment of interest will conflict with a nation's foreign aid programs.
D) payment of interest will necessarily have a deflationary effect on prices in the paying nation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "political business cycle" refers to the possibility that:
A) incumbent politicians will be re-elected regardless of the state of the economy.
B) politicians will manipulate the economy to enhance their chances of being re-elected.
C) there is more inflation during Liberal administrations than during Progressive Conservative administrations.
D) recessions coincide with election years.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effectiveness of the built-in or automatic stabilizers is limited because:
A) the stabilizers produce budget surpluses during recessions.
B) transfer payments and subsidies increase during inflation and decrease during recessions.
C) the offset which the stabilizers provide to a change in private spending is less than the change in private spending.
D) the stabilizers raise the general price level regardless of the phase of the business cycle.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the graph given below. 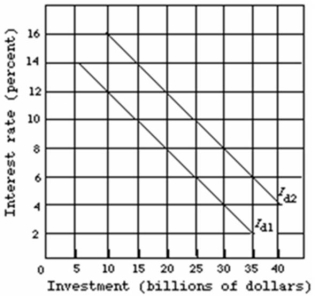 Assume that the investment demand curve of an economy is Id1 in period 1.The crowding-out effect of a large government deficit would be shown as a(n) :
Assume that the investment demand curve of an economy is Id1 in period 1.The crowding-out effect of a large government deficit would be shown as a(n) :
A) shift of the investment demand curve from Id1 to Id2.
B) leftward shift of the investment demand curve.
C) increase in the interest rate from 4 percent to 6 percent and a decline in investment spending of $5 billion.
D) increase in the interest rate from 6 percent to 8 percent and a decline in investment spending of $40 billion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are given the following information about aggregate demand at the existing price level for an economy: (1) consumption = $500 billion; (2) investment = $50 billion; (3) government purchases = $100 billion; and (4) net export = $20 billion.If the full-employment level of GDP for this economy is $620 billion, then what combination of actions would be most consistent with the goal of achieving price level stability?
A) increase government spending and taxes
B) decrease government spending and taxes
C) decrease government spending and increase taxes
D) increase government spending and decrease taxes
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discretionary fiscal policy will stabilize the economy most when:
A) deficits are incurred during recessions and surpluses during inflations.
B) the budget is balanced each year.
C) deficits are incurred during inflations and surpluses during recessions.
D) budget surpluses are continuously incurre
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The cyclically adjusted budget and the actual budget differ because the latter does not take government transfer payments into account.
B) The cyclically adjusted budget is less likely to show a deficit than is the actual budget.
C) The cyclically adjusted budget and the actual budget will show the same size deficit or surplus in any given fiscal year.
D) The cyclically adjusted budget is more likely to show a deficit than is the actual budget.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which set of events would best explain the effects of a contractionary fiscal policy on net exports?
A) It decreases domestic interest rates, causing the dollar to appreciate and net exports to decrease.
B) It decreases domestic interest rates, causing the dollar to depreciate and net exports to increase.
C) It decreases domestic interest rates, causing the dollar to depreciate and net exports to decrease.
D) It increases domestic interest rates, causing the dollar to appreciate and net exports to decrease.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which combination of fiscal policy actions would be most contractionary for an economy experiencing severe demand-pull inflation?
A) increase taxes and government spending
B) decrease taxes and government spending
C) increase taxes and decrease government spending
D) decrease taxes and increase government spending
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which are contractionary fiscal policies?
A) increased taxation and increased government spending
B) increased taxation and decreased government spending
C) decreased taxation and no change in government spending
D) no change in taxation and increased government spending
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which policy to finance the public debt might crowd-out private spending?
A) borrowing money from the public in the money market
B) decreasing government spending
C) creating new money
D) decreasing taxes
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The crowding-out effect refers to the possibility that deficit spending may lead people to increase their saving in anticipation of higher future taxes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A specific reduction in government spending will dampen demand-pull inflation by a greater amount, the:
A) smaller is the economy's MPC.
B) flatter is the economy's aggregate supply curve.
C) smaller is the economy's MPS.
D) less the economy's built-in stability.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cyclically adjusted budget deficit is also called a:
A) full- employment deficit.
B) cyclical deficit.
C) recession-caused deficit.
D) built-in stabilizer.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The lag between the time the need for fiscal action is recognized and the time action is taken is referred to as the:
A) crowding-out lag.
B) recognition lag.
C) operational lag.
D) administrative lag.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The financing of a government deficit increases interest rates and, as a result, reduces investment spending.This statement describes:
A) the supply-side effects of fiscal policy.
B) built-in stability.
C) the crowding-out effect.
D) the net export effect.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To understand the quantitative significance of the public debt relative to the economy, it should be:
A) divided by the social security trust fund.
B) multiplied by the size of the population.
C) measured as a percentage of GDP.
D) compared to the value of imports and exports.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Due to automatic stabilizers, when income decreases, government transfer spending:
A) increases and tax revenues decrease.
B) decreases and tax revenues increase.
C) and tax revenues decrease.
D) and tax revenues increase.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 234
Related Exams