A) 4CH3 + 6O2 4CO2 + 6H2O
B) 3CH4 + 6O2 3CO2 + 6H2O
C) 3CH3 + 6O2 3CO2 + 6H2O
D) 3CH4 + 5O2 3CO2 + 5H2O
E) 3CH4 + 6O2 3CO + 6H2O
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following ionic compounds would be expected to be insoluble in water?
A) NH4NO3
B) PbI2
C) NaCH3CO2
D) KCl
E) CuSO4
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the spectatorion(s) in the following reaction: Zn(s) + Cu(NO3) 2(aq) Cu(s) + Zn(NO3) 2(aq)
A) Cu2+(aq) and NO3-(aq)
B) Zn2+(aq) and Cu2+(aq)
C) Zn2+(aq) and NO3-(aq)
D) NO3-(aq) only
E) There are no spectatorions.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After the following equation is properly balanced, what is the coefficient in front of O2? S8(s) + O2(g) SO3(g)
A) 12
B) 8
C) 16
D) 3
E) 2
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If solutions of potassium chromate and calcium nitrate are mixed, will a double-displacement reaction occur? If so, what is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A) Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3) 2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
B) Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3) 2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaK(s)
C) No reaction will occur.
D) Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3) 2(aq) 2KNO3(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
E) Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3) 2(aq) K2(NO3) 2(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When writing a net ionic equation, how would Mg(NO3) 2(aq) be represented?
A) Mg2+(aq) + (NO3) 2-(aq)
B) Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq)
C) Mg(aq) + N2(aq) + 3O2(aq)
D) Mg2+(aq) + 2N3-(aq) + 6O2-(aq)
E) Mg2+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write and balance a net ionic equation for the reaction between iron(II) chloride and potassium hydroxide to form iron(II) hydroxide and potassium chloride.
A) Fe2Cl(aq) + OHˉ(aq) FeOH(s) + Clˉ(aq)
B) Fe2+(aq) + 2OHˉ(aq) Fe(OH) 2(s)
C) 2Clˉ(aq) + 2K+(aq) 2KCl(s)
D) 2Clˉ(aq) + 2K+(aq) 2K(s) + Cl2(g)
E) Fe2+(aq) + OHˉ(aq) FeOH(s)
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write and balance the equation for the combination reaction that occurs when solid potassium metal reacts with chlorine gas.
A) 2K(s) + Cl2(g) KCl(s)
B) K(s) + Cl(g) KCl(s)
C) 2K(s) + Cl2(g) 2ClK(s)
D) 2K(s) + Cl2(g) 2KCl(s)
E) K(s) + Cl2(g) KCl(s)
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When one compound is converted into two elements during a chemical reaction, a decomposition reaction has occurred.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the metals (Fe, Zn, Mg) will react in an aqueous solution of Al(NO3) 3 to produce aluminum metal?
A) Zn
B) Mg
C) Fe
D) None of these
E) All of these
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure shown, is a chemical reaction occurring? 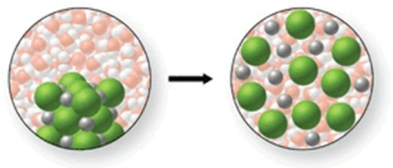
A) Yes, because the Na+ and Cl- ions are being removed from their ionic lattice as they are dissolved.
B) Yes, because the water molecules are reacting with the Na+ and Cl- ions to form a gas.
C) Yes, because a precipitate will be formed when the water and NaCl are mixed.
D) No, because there is no change occurring.
E) No, because the Na+ and Cl- ions are simply being surrounded by the water molecules as the salt dissolves.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solution of silver nitrate is mixed with a solution of sodium chloride, resulting in a precipitate of silver chloride and a solution of sodium nitrate.The class of this reaction is:
A) combination reaction.
B) double-displacement reaction.
C) decomposition reaction.
D) single-displacement reaction.
E) combustion reaction.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following chemical equations.Select the equations that represent chemical reactions, rather than physical changes.
A) I, II, and III
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I only
E) II and III only
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write and balance the equation for the decomposition reaction that occurs when solid copper(II) hydroxide, Cu(OH) 2, is heated.
A) Cu(OH) 2(s) Cu(s) + (OH) 2(g)
B) Cu(OH) 2(s) Cu(s) + 2OH(g)
C) 2Cu(OH) 2(s) 2CuO(s) + H2O(g)
D) Cu(OH) 2(s) Cu(s) + H2O(g)
E) Cu(OH) 2(s) CuO(s) + H2O(g)
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When heated, calcium carbonate (limestone) undergoes a decomposition reaction.Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
A) CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
B) CaCO3(s) Ca(s) + CO2(g)
C) 2CaCO3(s) 2CaO(s) + 3CO2(g)
D) CaCO3(s) Ca(s) + CO3(g)
E) 2CaCO3(s) 2CaO(s) + CO2(g)
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write and balance the equation for the combination reaction that occurs when aluminum metal reacts with oxygen gas.
A) 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) 2Al2O3(s)
B) 2Al(s) + 2O2(g) 2AlO2(s)
C) 2Al(s) + 2O2(g) Al2O3(s)
D) Al(s) + O2(g) AlO(s)
E) Al(s) + O2(g) AlO2(s)
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the reaction CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) .The driving force that causes the reaction to go to completion is:
A) formation of a soluble salt.
B) formation of an element.
C) formation of an insoluble gas.
D) formation of a precipitate.
E) none of these.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When aqueous solutions of hydrochloric acid and sodium carbonate are mixed,
A) CO2 gas is produced.
B) a precipitate is formed.
C) no reaction occurs.
D) H2 gas is formed.
E) sodium metal is formed.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When aqueous solutions of K2CO3 and CaCl2 are mixed, what is the correct formula for the precipitate that forms?
A) ClCO3(s)
B) KCl(s)
C) K2Cl2(s)
D) CaCO3(s)
E) K2Ca(s)
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When aqueous solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulfate are mixed, no reaction will occur.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 108
Related Exams