A) Clumped.
B) Unilateral.
C) Firm but freely movable.
D) Firm and nontender.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse notices that an infant has a large,soft lump on the side of his head and that his mother is very concerned.She tells the nurse that she noticed the lump approximately 8 hours after her baby's birth and that it seems to be getting bigger.One possible explanation for this is:
A) Hydrocephalus.
B) Craniosynostosis.
C) Cephalhematoma.
D) Caput succedaneum.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient says that she has recently noticed a lump in the front of her neck below her "Adam's apple" that seems to be getting bigger.During the assessment,the finding that leads the nurse to suspect that this may not be a cancerous thyroid nodule is that the lump (nodule) :
A) Is tender.
B) Is mobile and not hard.
C) Disappears when the patient smiles.
D) Is hard and fixed to the surrounding structures.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient reports excruciating headache pain on one side of his head,especially around his eye,forehead,and cheek that has lasted approximately 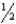 to 2 hours,occurring once or twice each day.The nurse should suspect:
to 2 hours,occurring once or twice each day.The nurse should suspect:
A) Hypertension.
B) Cluster headaches.
C) Tension headaches.
D) Migraine headaches.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient complains that while studying for an examination he began to notice a severe headache in the frontotemporal area of his head that is throbbing and is somewhat relieved when he lies down.He tells the nurse that his mother also had these headaches.The nurse suspects that he may be suffering from:
A) Hypertension.
B) Cluster headaches.
C) Tension headaches.
D) Migraine headaches.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mother brings in her newborn infant for an assessment and tells the nurse that she has noticed that whenever her newborn's head is turned to the right side,she straightens out the arm and leg on the same side and flexes the opposite arm and leg.After observing this on examination,the nurse tells her that this reflex is:
A) Abnormal and is called the atonic neck reflex.
B) Normal and should disappear by the first year of life.
C) Normal and is called the tonic neck reflex, which should disappear between 3 and 4 months of age.
D) Abnormal. The baby should be flexing the arm and leg on the right side of his body when the head is turned to the right.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse is performing an assessment on a 7-year-old child who has symptoms of chronic watery eyes,sneezing,and clear nasal drainage.The nurse notices the presence of a transverse line across the bridge of the nose,dark blue shadows below the eyes,and a double crease on the lower eyelids.These findings are characteristic of:
A) Allergies.
B) Sinus infection.
C) Nasal congestion.
D) Upper respiratory infection.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse suspects that a patient has hyperthyroidism,and the laboratory data indicate that the patient's T? and T? hormone levels are elevated.Which of these findings would the nurse most likely find on examination?
A) Tachycardia
B) Constipation
C) Rapid dyspnea
D) Atrophied nodular thyroid gland
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During an examination of a 3-year-old child,the nurse notices a bruit over the left temporal area.The nurse should:
A) Continue the examination because a bruit is a normal finding for this age.
B) Check for the bruit again in 1 hour.
C) Notify the parents that a bruit has been detected in their child.
D) Stop the examination, and notify the physician.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mother brings her 2-month-old daughter in for an examination and says,"My daughter rolled over against the wall,and now I have noticed that she has this spot that is soft on the top of her head.Is something terribly wrong?" The nurse's best response would be:
A) "Perhaps that could be a result of your dietary intake during pregnancy."
B) "Your baby may have craniosynostosis, a disease of the sutures of the brain."
C) "That 'soft spot' may be an indication of cretinism or congenital hypothyroidism."
D) "That 'soft spot' is normal, and actually allows for growth of the brain during the first year of your baby's life."
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When examining a patient's CN function,the nurse remembers that the muscles in the neck that are innervated by CN XI are the:
A) Sternomastoid and trapezius.
B) Spinal accessory and omohyoid.
C) Trapezius and sternomandibular.
D) Sternomandibular and spinal accessory.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse notices that a patient's palpebral fissures are not symmetric.On examination,the nurse may find that damage has occurred to which cranial nerve (CN) ?
A) III
B) V
C) VII
D) VIII
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse has just completed a lymph node assessment on a 60-year-old healthy female patient.The nurse knows that most lymph nodes in healthy adults are normally:
A) Shotty.
B) Nonpalpable.
C) Large, firm, and fixed to the tissue.
D) Rubbery, discrete, and mobile.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During an examination of a patient in her third trimester of pregnancy,the nurse notices that the patient's thyroid gland is slightly enlarged.No enlargement had been previously noticed.The nurse suspects that the patient:
A) Has an iodine deficiency.
B) Is exhibiting early signs of goiter.
C) Is exhibiting a normal enlargement of the thyroid gland during pregnancy.
D) Needs further testing for possible thyroid cancer.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient's laboratory data reveal an elevated thyroxine (T?) level.The nurse would proceed with an examination of the _____ gland.
A) Thyroid
B) Parotid
C) Adrenal
D) Parathyroid
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient has come in for an examination and states,"I have this spot in front of my ear lobe on my cheek that seems to be getting bigger and is tender.What do you think it is?" The nurse notes swelling below the angle of the jaw and suspects that it could be an inflammation of his:
A) Thyroid gland.
B) Parotid gland.
C) Occipital lymph node.
D) Submental lymph node.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During an assessment of an infant,the nurse notes that the fontanels are depressed and sunken.The nurse suspects which condition?
A) Rickets
B) Dehydration
C) Mental retardation
D) Increased intracranial pressure
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When examining the face of a patient,the nurse is aware that the two pairs of salivary glands that are accessible to examination are the ___________ and ___________ glands.
A) Occipital; submental
B) Parotid; jugulodigastric
C) Parotid; submandibular
D) Submandibular; occipital
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a well-baby checkup,the nurse notices that a 1-week-old infant's face looks small compared with his cranium,which seems enlarged.On further examination,the nurse also notices dilated scalp veins and downcast or "setting sun" eyes.The nurse suspects which condition?
A) Craniotabes
B) Microcephaly
C) Hydrocephalus
D) Caput succedaneum
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A male patient with a history of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) has come in for an examination and he states,"I think that I have the mumps." The nurse would begin by examining the:
A) Thyroid gland.
B) Parotid gland.
C) Cervical lymph nodes.
D) Mouth and skin for lesions.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 41
Related Exams