A) glycolysis.
B) the Krebs cycle.
C) the electron transport chain.
D) the Calvin cycle.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Alcohol is a by-product of fermentation by yeast.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Several energy carriers can be found in eukaryotic cells; the most versatile, as indicated in the illustration below, is 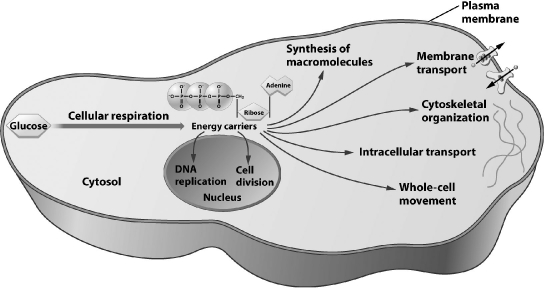
A) ATP.
B) NADPH.
C) NADH.
D) FADH₂.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The energy source that makes oxidative phosphorylation possible comes from
A) phosphate group transfers from ATP.
B) electrons transferred from NADPH.
C) electrons transferred from NADH.
D) electrons removed from CO2 during its oxidation.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Fermentation produces more ATP molecules than aerobic respiration does.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The muscles of a very active organism would contain fewer mitochondria than the muscles of a less active organism.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three stages of aerobic catabolism are
A) photosynthesis, glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation.
B) glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
C) glycolysis, fermentation, and the Krebs cycle.
D) photosynthesis, the Krebs cycle, and fermentation.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The mitochondria of plants contain thylakoids.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most Tibetans do not compensate for the low oxygen of their environment with an increase in red blood cells; perhaps their mitochondria have evolved a less oxygen-dependent method of catabolizing sugar and producing CO₂.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The green pigment most commonly associated with photosynthesis is ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells use a variety of metabolic pathways to construct ATP, but each concludes with the same step. Which of the following describes the final step by which ADP becomes ATP?
A) photosynthesis
B) phosphorylation
C) carbon fixation
D) electron transfer
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The conversion of inorganic carbon from air into the carbon atoms found in all living organisms is known as carbon ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The outcome of the Calvin cycle is the
A) capture of energy from sunlight.
B) synthesis of sugars like glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
C) production of pyruvate.
D) breakdown of complex molecules and the subsequent release of energy.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During exercise, the increase in respiration rate and heartbeat speed are driven by the need to replenish the oxygen used to support
A) lactic acid fermentation.
B) carbon dioxide synthesis in the lungs.
C) oxidative phosphorylation in muscle cell mitochondria.
D) in-the-dark reactions of photosynthesis.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The NADH produced by the Krebs cycle donates electrons to the electron transport chain.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is OK to say that your brain is solar powered, because
A) mitochondria in plant cells convert solar power to the chemical power that is used to run your brain.
B) cellular respiration is powered by sunlight.
C) the antenna complex in chloroplasts acts like a tiny solar panel, collecting sunlight to make the sugars that you consume to run your brain.
D) mitochondria in plant cells use solar power to split water molecules, creating the energy that runs your brain.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glycolysis occurs in the _____ of a cell.
A) nucleus
B) chloroplast
C) mitochondrion
D) cytosol
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During alcoholic fermentation, pyruvate is converted to ethanol in order to
A) increase the efficiency of cellular respiration by producing additional molecules of ATP.
B) release O2 as a by-product so that cellular respiration can continue.
C) create lactic acid to stimulate muscle contraction.
D) recycle NADH back into NAD+ so that the cell can continue glycolysis.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the process of photosynthesis, plants capture the kinetic energy of moving photons and transform it into potential energy in the form of
A) pyruvate.
B) stroma.
C) chemical bonds.
D) thylakoid disks.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process that produces ATP from sugars begins with glycolysis; when fatty acids are used the process begins with
A) oxidative phosphorylation.
B) the Calvin cycle.
C) the electron transport chain.
D) the Krebs cycle.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 84
Related Exams