A) liver.
B) urinary bladder.
C) kidney.
D) ureter.
E) urethra.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
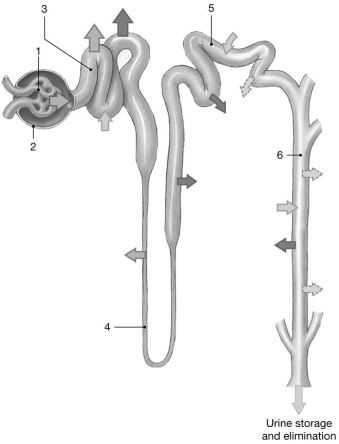 Figure 26-2 The Nephron
Use Figure 26-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area is sensitive to aldosterone?
Figure 26-2 The Nephron
Use Figure 26-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area is sensitive to aldosterone?
A) 2
B) 1
C) 4
D) 3
E) 5
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A transport mechanism that can move a substance against a concentration gradient by using cellular energy is
A) simple diffusion.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) bulk transport.
E) active transport.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glomerulonephritis may occur as a consequence of an infection with the bacterium
A) Clostridium difficile.
B) varicella.
C) Streptococcus.
D) MRSA.
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The position of the kidneys in the abdominal cavity is stabilized by
A) the overlying peritoneum.
B) contact with adjacent visceral organs.
C) supporting connective tissues.
D) the renal fascia.
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Triangular or conical structures located in the renal medulla are called
A) pyramids.
B) renal columns.
C) renal pelvises.
D) nephrons.
E) calyces.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under normal conditions,glomerular filtration depends on three main pressures.From the list below,what are these three main pressures? 1) blood hydrostatic pressure 2) capsular hydrostatic pressure 3) capsular colloid osmotic pressure 4) blood colloid osmotic pressure 5) urinary bladder hydrostatic pressure
A) 1,2,and 3 are correct.
B) 2,3,and 4 are correct.
C) 3,4,and 5 are correct.
D) 1,2,and 4 are correct.
E) 2,4,and 5 are correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ is the plasma concentration at which a specific compound will begin appearing in the urine.
A) tubular maximum
B) hydrostatic threshold
C) blood colloid maximum
D) osmotic pressure
E) renal threshold
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
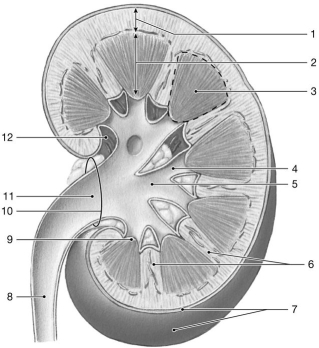 Figure 26-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 26-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "4."
Figure 26-1 The Structure of the Kidney
Use Figure 26-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "4."
A) renal pelvis
B) minor calyx
C) ureter
D) major calyx
E) renal column
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cells of the macula densa and the juxtaglomerular cells form the
A) renal corpuscle.
B) filtration membrane.
C) nephron loop (loop of Henle) .
D) juxtaglomerular complex.
E) afferent arteriole.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You complain to the doctor about constant pain and discomfort in the low back area.What test might logically be recommended?
A) an MRI
B) a pyelogram
C) a liver biopsy
D) an angiogram
E) a liver enzyme assay
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The region known as the macula densa is part of
A) the proximal convoluted tubule.
B) the distal convoluted tubule.
C) the collecting duct.
D) the nephron loop (loop of Henle) .
E) glomerular (Bowman's) capsule.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The renal veins drain into the
A) abdominal aorta.
B) renal arteries.
C) inferior vena cava.
D) segmental arteries.
E) peritubular capillaries.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the level of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) decreases,
A) a concentrated urine is produced.
B) less urine is produced.
C) the osmolarity of the urine decreases.
D) permeability to water in the collecting system increases.
E) water reabsorption increases in the loop of Henle.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glomerular (Bowman's) capsule and the glomerulus make up the
A) renal pyramid.
B) nephron loop (loop of Henle) .
C) renal corpuscle.
D) renal papilla.
E) collecting tubule system.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Substances secreted by the distal convoluted tubule include
A) hydrogen ions.
B) penicillin.
C) creatinine.
D) potassium ions.
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The urinary system regulates blood volume and pressure by
A) adjusting the volume of water lost in urine.
B) releasing erythropoietin.
C) releasing renin.
D) regulating NaCl levels in the blood.
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If heavy exercise reduces blood flow to the kidneys,which of the following might occur?
A) presence of protein in urine
B) presence of blood in urine
C) permanent kidney injury
D) damage to the glomeruli
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Major calyces are
A) large branches of the renal pelvis.
B) expanded ends of nephrons.
C) basic functional layers of the kidney.
D) conical structures that are located in the renal medulla.
E) the expanded ends of renal pyramids.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following substances undergo tubular secretion?
A) water
B) glucose
C) ammonium ions
D) sodium ions
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 129
Related Exams