A) It has a higher free energy content.
B) It has less chemical stability and is therefore more reactive.
C) It is more similar to the conformation of the substrate, as a result of induced fit.
D) It is energetically more stable, because it makes favorable interactions with the enzyme.
E) It participates in the reaction by exchanging a proton with the substrate, in a process that is known as general acid-base catalysis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neviripine is a drug for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection that is a noncompetitive inhibitor of reverse transcriptase.As a noncompetitive inhibitor, it:
A) Binds to the same site on the enzyme as the substrate.
B) Reduces the Km of the substrate.
C) Forms a covalent bond with the enzyme.
D) Does not bond to the enzyme in the absence of substrate.
E) Moves the intercept on the 1/v axis of the Lineweaver-Burk plot farther away from the X-Y intersection.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
C.G.is a 30-year-old retired stockbroker who has developed possible skin cancer while sailing in Polynesia.A skin biopsy is analyzed for cyclin-dependent kinase activity at different concentrations of the cosubstrate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) .The results are shown in Figure 4.7. 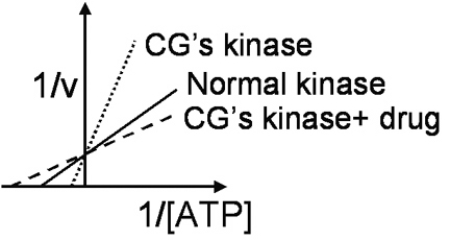 The apparent effect of the drug on C.G.'s kinase activity is to:
The apparent effect of the drug on C.G.'s kinase activity is to:
A) Reduce the Vmax of the enzyme.
B) Increase the Vmax of the enzyme.
C) Reduce the Km of the enzyme.
D) Increase the Km of the enzyme.
E) Allosterically activate the kinase.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The maximal reaction rate (Vmₐₓ) is a kinetic property of an enzymatic reaction that depends on the incubation conditions, the enzyme concentration, and:
A) The standard free energy change (DG0') of the reaction.
B) The entropy change that accompanies the reaction.
C) The ratio between the kinetic rate constants for the forward and backward reactions.
D) Km.
E) The turnover number of the enzyme.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most NAD-using enzymes are named as:
A) Transferases.
B) Dehydrogenases.
C) Carboxylases.
D) Oxygenases.
E) Lyases.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate of a typical enzyme-catalyzed reaction:
A) Is independent of pH over a broad range of pH values.
B) Is approximately proportional to the substrate concentration as long as the substrate concentration is much lower than the Michaelis constant (Km) .
C) Rises by a factor of about 4 when the temperature is raised by 10° C.
D) Is no longer affected by the enzyme concentration at saturating substrate concentrations.
E) Is virtually independent of the temperature, as long as heat denaturation is avoided.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Data are plotted for the action of a histone-modifying enzyme (solid lines) in two graph formats in Figure 4.10.Dashed lines indicate the data for the enzyme in the presence of an effector molecule, deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP) . 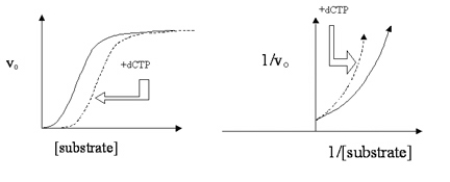 Which statement is not true regarding this enzyme, its substrate (histone protein) , and its effector dCTP?
Which statement is not true regarding this enzyme, its substrate (histone protein) , and its effector dCTP?
A) The effector dCTP increases the Km.
B) The enzyme is under allosteric control.
C) The influence of the effector is reduced at high substrate (histone) concentrations.
D) The enzyme obeys Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
E) dCTP is an inhibitory effector of enzyme activity.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction (where ADP = adenosine diphosphate) belongs to which broad enzyme class? Protein + ATP → Phosphoprotein + ADP
A) Isomerase.
B) Lyase.
C) Oxidoreductase.
D) Transferase.
E) Ligase.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is characteristic for the active sites of enzymes?
A) Nearly all amino acid side chains of the protein participate in catalysis.
B) The amino acid residues that form the active site are adjacent in the primary structure of the polypeptide.
C) The amino acid residues in the active site that bind the substrate are always the ones that catalyze the reaction.
D) In many cases, the active site changes its conformation when the substrate binds.
E) In many cases, the initial binding of the substrate to the active site involves the formation of a covalent bond.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Racemase enzymes interconvert:
A) Epimers.
B) Anomers.
C) Enantiomers.
D) Diasteriomers.
E) Aldoses and ketoses.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "catalytic triad" in the active site of the serine protease thrombin contains the three amino acids:
A) Aspartate, glutamate, histidine.
B) Cysteine, arginine, serine.
C) Glutamate, histidine, tryptophan.
D) Serine, histidine, aspartate.
E) Threonine, asparagine, tyrosine.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cold virus produces an enzyme rhinase, which is acted upon by a drug called rhinex.Rhinex is known to be a noncompetitive inhibitor of the viral enzyme.Which of the dashed lines in Figure 4.8 describes the action of the enzyme in the presence of drug? The solid line describes the action of the drug-free enzyme. 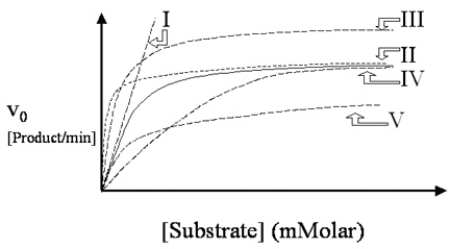
A) I.
B) II.
C) III.
D) IV.
E) V.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alanine transaminase is a liver enzyme important in assessment of liver function.Figure 4.12 shows the "V vs.[S]" curve for the normal enzyme (solid line) and the same enzyme in the presence of the enzyme inhibitor 2-aminobutanoic acid (dashed line) . ![Alanine transaminase is a liver enzyme important in assessment of liver function.Figure 4.12 shows the V vs.[S] curve for the normal enzyme (solid line) and the same enzyme in the presence of the enzyme inhibitor 2-aminobutanoic acid (dashed line) . Which is true regarding the inhibitor 2-aminobutanoic acid? A) It is a noncompetitive inhibitor. B) It is an uncompetitive inhibitor. C) It is a positive allosteric effector that binds outside the active site. D) It is a competitive inhibitor. E) It is an irreversible (suicide) inhibitor.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4957/11ea53cd_d364_2d0d_8094_279d18de7820_TB4957_00.jpg) Which is true regarding the inhibitor 2-aminobutanoic acid?
Which is true regarding the inhibitor 2-aminobutanoic acid?
A) It is a noncompetitive inhibitor.
B) It is an uncompetitive inhibitor.
C) It is a positive allosteric effector that binds outside the active site.
D) It is a competitive inhibitor.
E) It is an irreversible (suicide) inhibitor.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tadalafil (Cialis) is a competitive inhibitor of phosphodiesterase type 5.As a competitive inhibitor, you can expect tadalafil to:
A) Covalently modify the enzyme.
B) Bind to allosteric sites on the enzyme.
C) Lower the Vmax of the reaction.
D) Increase the Km of the enzyme for the substrate.
E) Reduce the free energy of activation for the reaction.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two different subtypes of matrix metalloproteinase, enzymes MMP-2 and MMP-9, are released from a squamous cell carcinoma.The enzymes behave according to Michaelis-Menten kinetics by the measured parameters in the table, in the same substrate:  Оn the basis of these data, which of the following is a true statement?
Оn the basis of these data, which of the following is a true statement?
A) MMP-2 makes more product than MMP-9 at the same enzyme concentrations.
B) MMP-2 is more stable to proteolytic degradation than MMP-9.
C) MMP-2 is denatured in the extracellular environment faster than MMP-9.
D) MMP-2 is more active at its maximal velocity than MMP-9.
E) MMP-2 reaches half-maximal velocity at a higher substrate concentration than does MMP-9.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is true for enzymes in general?
A) They reduce the free energy of the product in relation to that of the substrate.
B) They can catalyze their reaction over a wide pH range.
C) They increase the rate of the forward and backward reactions in proportion.
D) When the substrate is chiral, both isomeric forms can be used as substrates of the enzymatic reaction.
E) They alter the position of the equilibrium for a reaction.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aldehyde groups are present in some metabolites.These aldehyde groups are most likely to be metabolized with the help of which type of enzyme?
A) Monooxygenase.
B) Dehydrogenase.
C) Kinase.
D) Synthetase.
E) Hydrolase.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term ligase refers to a class of enzymes that catalyzes:
A) Hydrogen transfer reactions.
B) The transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another.
C) The removal of a group, forming a C=C double bond in the substrate.
D) The joining together of two molecules.
E) Cleavage of a bond.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Thiol proteases cleave peptide bonds by a mechanism similar to that of serine proteases, such as trypsin and chymotrypsin, but they contain cysteine instead of serine.In which way does the sulfhydryl group of cysteine participate in the reaction?
A) It participates in substrate binding and thereby helps determine the substrate specificity of the enzyme.
B) It reacts covalently with the side chain of an acidic amino acid residue in the substrate.
C) It attacks the C=O portion of a peptide bond and forms a thioester with it.
D) It relays electrons to the peptide bond of the substrate, thereby facilitating the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate.
E) It forms a transient disulfide bond with a cysteine side chain of the substrate.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A liver enzyme called two-substrate inactivates a drug by the following reaction, where NADP is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and NADPH is the reduced form of NADP: Drug + NADPH ? Inactive product + NADP⁺
The Km and physiological substrate concentrations (both in millimoles per liter) are given in the table for both substrates. ![A liver enzyme called two-substrate inactivates a drug by the following reaction, where NADP is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and NADPH is the reduced form of NADP: Drug + NADPH ? Inactive product + NADP⁺ The Km and physiological substrate concentrations (both in millimoles per liter) are given in the table for both substrates. What is the rate-limiting substrate under these conditions, and what is the derived Michaelis-Menten equation that describes the velocity of product formation by the enzyme? A) Drug limiting; vo = Vmax. B) NADPH limiting; 1/2 Vmax. C) NADPH limiting; (Vmax x [NADPH]) /0.22 mmol. D) Drug limiting; (Vmax x [Drug]) /0.12 mmol. E) NADPH limiting; k2/Km.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4957/11ea53cd_d364_05fb_8094_1798e1df3f2a_TB4957_00.jpg) What is the rate-limiting substrate under these conditions, and what is the derived Michaelis-Menten equation that describes the velocity of product formation by the enzyme?
What is the rate-limiting substrate under these conditions, and what is the derived Michaelis-Menten equation that describes the velocity of product formation by the enzyme?
A) Drug limiting; vo = Vmax.
B) NADPH limiting; 1/2 Vmax.
C) NADPH limiting; (Vmax x [NADPH]) /0.22 mmol.
D) Drug limiting; (Vmax x [Drug]) /0.12 mmol.
E) NADPH limiting; k2/Km.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 20
Related Exams