A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) movement from B to A
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) movement from A to B
E) a shift from line 3 to line 2
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gap between the real and nominal interest rate represents:
A) the inflationary premium.
B) the time preference
C) the difference from what the lender receives and the borrower pays.
D) consumption smoothing.
E) a surplus of loanable funds.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume households become thriftier.This would cause:
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) the supply of loanable funds to decrease.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If real rates were higher than nominal rates in 2009,the implication is that:
A) inflation was greater than the real rate.
B) inflation was less than the real rate.
C) the nominal rate was equal to the real rate.
D) inflation was negative (deflation was occurring) .
E) the real rate was equal to the rate of inflation.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wealth increases in the United States because the value of the stock market increases; if all else is equal,this would cause:
A) a larger gap between the real and nominal rates of interest.
B) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
C) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) the supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) corporations to be more willing to borrow.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which description best indicates a fall in interest rates?
A) This would be shown by a downward movement along both the demand and supply curves for loanable funds.
B) This would be shown by a downward movement along the demand curve for loanable funds but in a leftward shift in the supply curve for loanable funds.
C) This would be shown by a downward movement along the supply curve for loanable funds but in a rightward shift in the demand curve for loanable funds.
D) This would be shown by a leftward shift in the supply curve for loanable funds but in a rightward shift in the demand curve for loanable funds.
E) This would be shown by an upward movement along both the demand and supply curves for loanable funds.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two nations are located next to one another.In Nation A,people are very thrifty and spend much less than their incomes; moreover,Nation A's government runs a balanced budget every year.In Nation B,people spend all of their income,but their government runs consistent deficits.Thus:
A) Nation A's extra savings would increase the supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
B) Nation B's government deficit would be a supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
C) Nation A's extra savings would increase the demand for loanable funds in Nation B.
D) Nation B would instantly default on all of its debt obligations.
E) Nation A's extra savings would decrease the supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inflation reached its peak (of at least 14%) in the late 1970s/early 1980s.If this statement is true,then:
A) it is certain the real rate of interest was greater than the nominal rate.
B) it is certain the nominal rate of interest was greater than the real rate.
C) borrowers would borrow more because, automatically, real rates would fall.
D) the real rate of interest must have been constant, even if the nominal rate varied because of consumption smoothing.
E) if higher nominal rates were charged, it would be certain that higher real rates would be received.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume foreign incomes rise.Ceteris paribus (all things equal) ,this would cause:
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) the demand of loanable funds to decrease.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smiley Myrus owns a large corporation that is building a new shopping mall in Winston-Salem,North Carolina.In all likelihood:
A) Smiley's firm is a supplier of loanable funds.
B) Smiley's firm pays a higher rate of interest than most borrowers, based on the Fisher equation.
C) Smiley's firm is a borrower of loanable funds.
D) Smiley's firm pays a lower rate of interest than most borrowers, based on the Fisher equation.
E) Smiley's firm would loan its profits to foreign entities.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate represents:
A) the opportunity cost of saving.
B) the opportunity cost of consumption.
C) the opportunity cost of saving plus the opportunity cost of inflation.
D) only the opportunity cost of taking a different job.
E) the price of savings, but not investment.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate is:
A) the price of labor.
B) the price of land.
C) both the price of capital and the price of labor.
D) the price of loanable funds.
E) the marginal rate of investment supply.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume you put money into an asset that pays you 7% interest and inflation is 5%.Which statement is correct?
A) This means the nominal rate of interest is 7% and the real rate is 5%.
B) This means the real rate of interest is 2%.
C) The textbook states that all interest rates would be assumed to be the real rate; thus, the nominal rate is 12%.
D) This means the nominal rate of interest is 35%.
E) If the rate of inflation falls, your real rate of interest from this asset would also fall.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most people have a time preference.Since this is true:
A) they must earn interest to consume now (save later) and are willing to pay interest to consume later (save now) .
B) they must be paid interest to consume later (save now) and are willing to pay interest to consume now (save later) .
C) they are willing to accept simple interest in the short run but only compound interest in the long run.
D) they will accept positive rates of interest on checking accounts and negative rates of interest on savings accounts.
E) they prefer more free time to less free time.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Those with the least patience:
A) have the greatest time preference.
B) have the least time preference.
C) will demand a higher nominal interest rate but not a higher real rate.
D) will save the most.
E) will engage in the most consumption smoothing.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following graph to answer the next five questions:
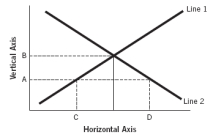 -Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,and that point C represents 40 and point D represents 80,then it would be true that:
-Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,and that point C represents 40 and point D represents 80,then it would be true that:
A) both points represent interest rates and there is a surplus of loanable funds at an 80% interest rate.
B) both points represent interest rates and there is a shortage of loanable funds at an 80% interest rate.
C) both points represent the quantity of loanable funds and there would be a surplus of loanable funds of 40 units.
D) both points represent the quantity of loanable funds and at interest rate A there would be a shortage of loanable funds of 40 units.
E) the quantity of loanable funds supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at interest rate B, if B represents an interest rate.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the market for loanable funds is in equilibrium at 5% interest.Assuming that firms become more pessimistic about future profits,all else being equal:
A) the equilibrium interest rate would rise and the equilibrium quantity would fall.
B) both the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity would rise.
C) both the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity would fall.
D) the equilibrium interest rate would fall and the equilibrium quantity would rise.
E) the equilibrium real rate of interest would become negative and the equilibrium quantity would remain unchanged.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The measurement of personal savings may be distorted by:
A) increased college tuition costs.
B) reduced college tuition costs.
C) higher marginal tax rates.
D) greater levels of home equity.
E) lower levels of home equity.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Savings is:
A) the demand for loanable funds and is downward sloping.
B) the supply of loanable funds and is horizontal.
C) the supply of loanable funds and is vertical.
D) the supply of loanable funds and is upward sloping.
E) the demand for loanable funds and is upward sloping.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If household wealth rises and capital becomes less productive,we would correctly say that:
A) the new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds would decrease, but we would be unable to tell if the new equilibrium interest rate would be higher or lower than the original.
B) the new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds would increase, but we would be unable to tell if the new equilibrium interest rate would be higher or lower than the original.
C) the new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds would be indeterminate, but we would be certain the new equilibrium interest rate would be higher than the original.
D) the new equilibrium quantity of loanable funds would be indeterminate, but we would be certain the new equilibrium interest rate would be less than the original.
E) based on this information and because both changes would affect the demand for loanable funds in the opposite way, we would be unable to say anything about the relationship of the new equilibrium interest rate and quantity to the original interest rate and quantity.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 139
Related Exams