A) ozone
B) nitrogen oxides
C) carbon monoxide
D) volatile organic compounds
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acid rain concentrated in the eastern portions of the United States is primarily the result of
A) nuclear power plants in the region.
B) coal-burning power plants in the Midwest.
C) coal-burning power plants in northeastern Canada.
D) off-shore oil drilling rigs along the east coast of the United States.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
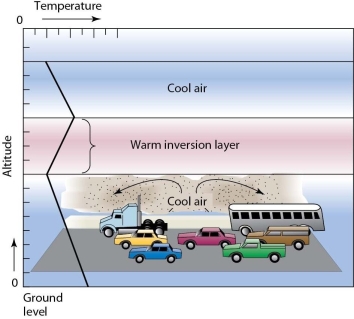 -The conditions represented in this figure illustrate
-The conditions represented in this figure illustrate
A) a temperature inversion.
B) stratospheric smog.
C) the greenhouse effect.
D) how high levels of ozone affect climate near the ground.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As demonstrated during the high oil prices of 2008,when gasoline prices skyrocket,hybrid vehicle sales
A) decrease and more people use public transportation.
B) increase and fewer people use public transportation.
C) decrease and fewer people use public transportation.
D) increase and more people use public transportation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a major anthropogenic source of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) ?
A) coal-fired electrical generating plants
B) agricultural fertilizers
C) incompletely combusted fossil fuels from vehicle exhaust
D) nuclear power plants
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ozone levels can increase in the troposphere when
A) VOCs are present.
B) PANs react with atmospheric nitrogen to form ozone.
C) VOCs release ozone when they are broken apart by solar energy.
D) more carbon dioxide is available to contribute additional oxygen for ozone formation.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Atmospheric scientists often measure gases in parts per million by weight (ppm) .If CO₂ is currently 0.04% of the atmosphere,the level expressed in ppm is
A) 4 ppm.
B) 4000 ppm.
C) 400 ppm.
D) 0.004 ppm.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A temperature inversion occurs when
A) high levels of sunshine burn off a fog.
B) regions experience high winds and intense sunshine.
C) the air near the ground is cooler than the air directly above it.
D) the air near the ground is warmer than the air at higher altitudes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are primary pollutants that frequently occur undetected in homes?
A) radon and carbon monoxide
B) soot,smoke,and salt aerosols
C) peroxyacetyl nitrate and sulfur dioxide
D) volatile organic compounds and peroxyacetyl nitrate
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Asthma is a serious and widespread disease related to air pollution.Symptoms of asthma include impaired breathing resulting from constricted air passages,a disorder of the
A) digestive system.
B) cardiovascular system.
C) endocrine system.
D) immune system.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Crop damage from ozone formation is most likely to occur
A) downwind of a large urban center in the summer.
B) upwind of large polluting regions in the spring.
C) next to busy major highways in the winter
D) downwind from an ocean shoreline in the spring.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On May 18,1980,a massive eruption of Mt.St.Helens in Washington State sent a huge plume of ash high into the air.Over the next two weeks,the ash traveled around the world.To move that far,the ash would have to
A) dissolve in the nitrogen of the air.
B) combine with moisture in the troposphere.
C) bind to aerosols in the lithosphere.
D) reach into the stratosphere.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most of the public health impacts from air pollution are the result of
A) acute exposure to a single pollutant.
B) acute exposure to many pollutants.
C) chronic exposure to a single pollutant.
D) chronic exposure to many pollutants.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Air pollution in a heavily industrialized region would be reduced and the air would be healthier if that region
A) received more rain.
B) received less sunshine.
C) were at least 200 miles from an ocean.
D) used more coal to generate electricity.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most recently discovered air pollutant that is a stratospheric ozone destroying molecule is
A) CO.
B) sulfur oxides.
C) VOCs.
D) nitrous oxide (N₂O) .
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reading through the long list of health effects of smoking tobacco,a student is shocked to find that smokers are inhaling carbon monoxide.Which of the following symptoms is most related to this particular component of tobacco smoke?
A) shortness of breath
B) fibrosis of the lungs
C) chronic bronchitis
D) suppressed immune functions
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming that these people do not use tobacco products,a person in which of the following professions would most likely have the highest exposure to benzene,a known carcinogen?
A) a truck driver or pharmaceutical company worker
B) a cashier at a grocery store
C) an accountant working in a large office building
D) a psychology professor
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The complete combustion of fossil fuels and refuse produces
A) radon and carbon monoxide.
B) volatile organic compounds.
C) sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
D) carbon dioxide and water vapor.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 1948 in Donora,Pennsylvania,the routine release of toxins into the air became a deadly fog because of
A) a chemical spill in the nearby Monongahela River.
B) greatly increased activity of the nearby industries.
C) a thermal inversion and stagnant weather conditions.
D) the failure of the chemical scrubbing systems on smokestacks.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nearly 300 million years ago,dragonflies existed that were the size of large hawks today.Some scientists believe that these giants could fly then,but not today,because oxygen in the atmosphere was much higher.If oxygen levels 300 million years ago were 50% higher than today,what percentage of the atmosphere would have consisted of oxygen for these giant dragonflies?
A) 30%
B) 20%
C) 10%
D) 2%
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 89
Related Exams