A) large, so that prices at potential GDP are below expectations and people can afford to buy enough goods to support the natural level of employment
B) large enough that prices at potential GDP are above expectations and firms can afford to hire workers
C) small, so that prices at potential GDP are below expectations and people can afford to buy enough goods to support the natural level of employment
D) small, so that prices at potential GDP are above expectations and firms can afford to hire the workers
E) exactly the size that makes prices equal to the prices people expected to prevail
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One reason that long time lags hamper the effectiveness of economic policy is that
A) people don't want to wait for economic recovery
B) the longer unemployment lasts the more intense inflation becomes
C) by the time the impact of a policy is felt, a new problem may have come along that requires a different policy, which may make the economic situation even worse
D) if inflation is allowed to continue for too long, it becomes immune to policy interference
E) if unemployment is allowed to continue for too long, it becomes immune to policy interference
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Along the short-run Phillips curve, when the unemployment rate goes down,
A) unemployment benefit payments go up
B) prices go down
C) the Phillips curve shifts outward
D) the inflation rate goes up
E) there is no change in the rate of inflation
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the natural rate hypothesis, the economy tends toward
A) the natural rate of unemployment in the long run
B) the natural rate of unemployment in the short run
C) potential output in the short run
D) zero inflation in the long run
E) a stable tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the long run
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose we observe several years of falling inflation rates for an economy. Which of the following would best explain this phenomenon?
A) Unemployment is probably at the natural rate.
B) The unemployment rate must be rising.
C) The unemployment rate must be below the natural rate.
D) The unemployment rate is probably above the natural rate.
E) Aggregate output must be increasing.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Advocates of policy rules rather than discretion believe that self-correction forces work too slowly when discretionary policy is used.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a potential problem with active policy for policy makers?
A) predicting what would happen with a passive approach
B) lacking the tools needed to achieve the desired result quickly
C) not predicting the effects of an active policy on the economy's key performance measures
D) fiscal and monetary policy makers not working together
E) failing to implement the appropriate policy because of political obstacles
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If self-correction causes prices to fall less than nominal wages, both output and real wages will decrease.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the time for an economy to self-correct is shorter than the active policy lags,
A) active policy should be strengthened
B) active policy will likely be destabilizing
C) the passive policy case is weakened
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts more rapidly than the short-run aggregate supply curve
E) active policy will work better than passive policy
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rational expectations school advocates
A) monetarism
B) Keynesianism
C) the use of fiscal policy
D) the use of monetary policy
E) a passive approach to policy
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rational expectations school advocates the passive rule of a fixed-growth-rate monetary policy because
A) we don't have enough information to pursue an active policy
B) the economy is not in bad enough shape to require active intervention
C) then the Federal Reserve Board would be superfluous and we could eliminate a large bureaucracy
D) people render active policy ineffective by figuring out what it's going to be and taking actions to offset it
E) they prefer to put their major emphasis on an active fiscal policy
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the actual inflation rate exceeds the expected inflation rate,
A) the economy is on the long-run Phillips curve
B) unemployment exceeds the natural rate
C) maintaining the existing unemployment rate will require increasing inflation in the long run
D) the actual rate will tend to fall toward the expected rate
E) unemployment will tend to decrease in the long run
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy experiencing an expansionary gap
A) operates in an environment in which labor shortages drive up money wages, real wages, and prices
B) results in an excess supply of labor due to rising money wages and prices
C) will self-correct as rising money wages decrease faster than rising prices
D) will experience rising money wages and prices but falling real wages
E) will have excessive involuntary unemployment (e.g., cyclical unemployment)
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time it takes for the Fed's purchase of government securities to ultimately change aggregate demand is called the
A) recognition lag
B) implementation lag
C) effectiveness lag
D) decision-making lag
E) self-correction lag
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 17-2 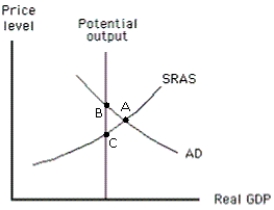 -According to those who favor a passive approach to policy, how will the economy shown in Exhibit 17-2 attain equilibrium at potential output?
-According to those who favor a passive approach to policy, how will the economy shown in Exhibit 17-2 attain equilibrium at potential output?
A) The SRAS curve will shift to the left.
B) The SRAS curve will shift to the right.
C) Either the money supply or government spending should be increased.
D) Either the money supply or government spending should be decreased.
E) Aggregate demand should be decreased.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 17-1 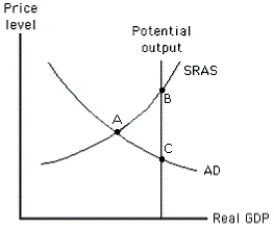 -According to those who favor an active approach to policy, where will the economy in Exhibit 17-1 end up when it achieves its potential output?
-According to those who favor an active approach to policy, where will the economy in Exhibit 17-1 end up when it achieves its potential output?
A) point A
B) point B
C) point C
D) either point B or C
E) cannot tell from the information provided
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about the recession of the early 1990s?
A) The recession was triggered by Iraq's invasion of Kuwait
B) Because of large federal deficits, policy makers were reluctant to adopt discretionary fiscal policy to revive the economy
C) President George H. W. Bush advocated a passive approach
D) Presidential candidate Bill Clinton advocated an active approach
E) All of the answers are correct
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 17-4 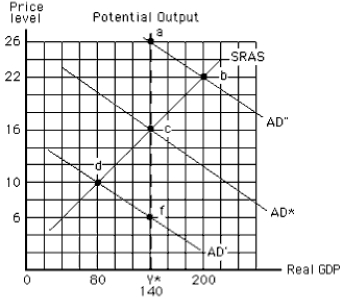 -If the economy in Exhibit 17-4 is initially at point c and aggregate demand is stable, the economy will
-If the economy in Exhibit 17-4 is initially at point c and aggregate demand is stable, the economy will
A) move toward point a
B) move toward point b
C) stay at point c
D) move toward point d
E) move toward point f
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The selection of a new policy takes place during a period of time known as the
A) activity lag
B) decision-making lag
C) effectiveness lag
D) implementation lag
E) recognition lag
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the natural rate hypothesis,
A) government policy makers can influence the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the long run but not in the short run
B) government policy makers can target both stable interest rates and a stable money supply in the long run but not in the short run
C) government policy makers can target both stable interest rates and a stable money supply in the short run but not in the long run
D) the economy tends toward the natural rate of unemployment only when the government provides the appropriate demand stimulus
E) government policy makers can influence the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the short run but not in the long run
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 190
Related Exams