A) 0.46 m 0.47 m
B) 0.30 m 0.54 m
C) 0.42 m 0.60 m
D) 0.47 m 0.26 m
E) 0.60 m 0.42 m
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A football player kicks a 0.41-kg football initially at rest; and the ball flies through the air. If the kicker's foot was in contact with the ball for 0.051 s and the ball's initial speed after the collision is 21 m/s, what was the magnitude of the average force on the football?
A) 9.7 N
B) 46 N
C) 81 N
D) 170 N
E) 210 N
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A machine gun fires 25-g bullets at the rate of 4 bullets per second. The bullets leave the gun at a speed of 1000 m/s. What is the average recoil force experienced by the machine gun?
A) 10 N
B) 20 N
C) 100 N
D) 200 N
E) 1000 N
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg pistol fires a 1.0-g bullet with a muzzle speed of 1000 m/s. The bullet then strikes a 10-kg wooden block resting on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block and the embedded bullet then slide across the surface.  -What is the kinetic energy of the bullet as it travels toward the block?
-What is the kinetic energy of the bullet as it travels toward the block?
A) 100 J
B) 500 J
C) 1000 J
D) 5000 J
E) 10 000 J
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bat strikes a 0.050-kg baseball so that its velocity changes by +32 m/s in 0.080 s. With what average force was the ball struck?
A) +20 N
B) -20 N
C) +200 N
D) -200 N
E) +10 N
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A comet fragment of mass 1.96 × 1013 kg is moving at 6.50 × 104 m/s when it crashes into Callisto, a moon of Jupiter. The mass of Callisto is 1.08 × 1023 kg. The collision is completely inelastic. -How much kinetic energy was released in the collision?
A) 8.28 × 1022 J
B) 3.51 × 1027 J
C) 7.02 × 1027 J
D) 4.14 × 1022 J
E) 1.50 × 1013 J
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rock is dropped from a high tower and falls freely under the influence of gravity. Which one of the following statements concerning the rock as it falls is true? Neglect the effects of air resistance.
A) The rock will gain an equal amount of momentum during each second.
B) The rock will gain an equal amount of kinetic energy during each second.
C) The rock will gain an equal amount of speed for each meter through which it falls.
D) The rock will gain an equal amount of momentum for each meter through which it falls.
E) The amount of momentum the rock gains will be proportional to the amount of potential energy that it loses.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 4.0-kg block slides along a frictionless surface with a constant speed of 5.0 m/s as shown. Two seconds after it begins sliding, a horizontal, time-dependent force is applied to the mass. The force is removed eight seconds later. The graph shows how the force on the block varies with time. 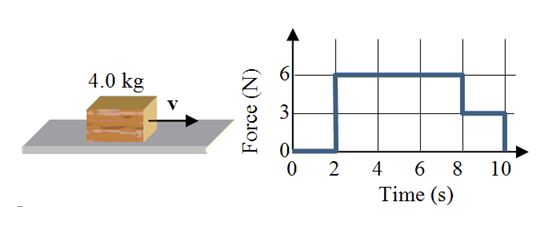 -What, approximately, is the speed of the block at t = 11 seconds?
-What, approximately, is the speed of the block at t = 11 seconds?
A) 5.0 m/s
B) 16 m/s
C) 25 m/s
D) 65 m/s
E) 75 m/s
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 160-kg space probe is moving in the positive x direction at 18 km/s when it encounters a time-dependent force directed in the negative x direction. The force is as follows:
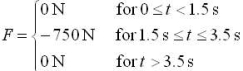 Determine the final speed of the space probe.
Determine the final speed of the space probe.
A) 8.6 km/s
B) 5.3 km/s
C) 11 km/s
D) 16 km/s
E) 23 km/s
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the game of billiards, all the balls have approximately the same mass, about 0.17 kg. In the figure, the cue ball strikes another ball such that it follows the path shown. The other ball has a speed of 1.5 m/s immediately after the collision. What is the speed of the cue ball after the collision? 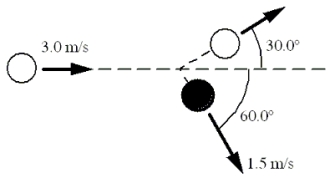
A) 1.5 m/s
B) 1.8 m/s
C) 2.6 m/s
D) 4.3 m/s
E) 5.2 m/s
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.5-kg ball and a 5.0-kg ball have an elastic collision. Before the collision, the 2.5-kg ball was at rest and the other ball had a speed of 3.5 m/s. What is the kinetic energy of the 2.5-kg ball after the collision?
A) 1.7 J
B) 3.4 J
C) 8.1 J
D) 14 J
E) 27 J
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 0.065-kg tennis ball moving to the right with a speed of 15 m/s is struck by a tennis racket, causing it to move to the left with a speed of 15 m/s. If the ball remains in contact with the racquet for 0.020 s, what is the magnitude of the average force exerted on the ball?
A) zero newtons
B) 98 N
C) 160 N
D) 240 N
E) 320 N
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A space vehicle of mass m has a speed v. At some instant, it separates into two pieces, each of mass 0.5m. One of the pieces is at rest just after the separation. -How much work was done by the internal forces that caused the separation?
A) zero joules
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) mv2
E) 2mv2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While on an interplanetary mission, a 58.5-kg astronaut is floating toward the front of her ship at 0.15 m/s, relative to the ship. She wishes to stop moving, relative to the ship. She decides to throw away the 2.50-kg book she's carrying. What should the approximate speed and direction of the book be to achieve her goal?
A) 0.15 m/s, toward the front of the ship
B) 3.5 m/s, toward the back of the ship
C) 3.7 m/s, toward the front of the ship
D) 0.30 m/s, toward the back of the ship
E) 1.5 m/s, toward the front of the ship
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A space vehicle of mass m has a speed v. At some instant, it separates into two pieces, each of mass 0.5m. One of the pieces is at rest just after the separation. -Which one of the following statements concerning this situation is true?
A) The moving piece has speed 2v.
B) This process conserves kinetic energy.
C) The piece at rest possesses kinetic energy.
D) The process does not conserve total energy.
E) This process does not conserve momentum.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 3.0-kg cart moving to the right with a speed of 1.0 m/s has a head-on collision with a 5.0-kg cart that is initially moving to the left with a speed of 2.0 m/s. After the collision, the 3.0-kg cart is moving to the left with a speed of 1.0 m/s. What is the final velocity of the 5.0-kg cart?
A) zero m/s
B) 0.80 m/s to the right
C) 0.80 m/s to the left
D) 2.0 m/s to the right
E) 2.0 m/s to the left
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A stationary 4-kg shell explodes into three pieces. Two of the fragments have a mass of 1 kg each and move along the paths shown with a speed of 10 m/s. The third fragment moves upward as shown. 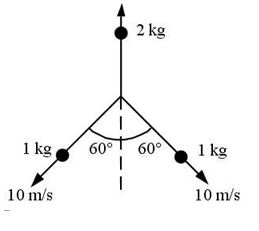 -What is the speed of the center of mass of this system after the explosion?
-What is the speed of the center of mass of this system after the explosion?
A) zero m/s
B) 1 m/s
C) 3 m/s
D) 5 m/s
E) 7 m/s
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 50.0-kg boy runs at a speed of 10.0 m/s and jumps onto a cart as shown in the figure. The cart is initially at rest. If the speed of the cart with the boy on it is 2.50 m/s, what is the mass of the cart? 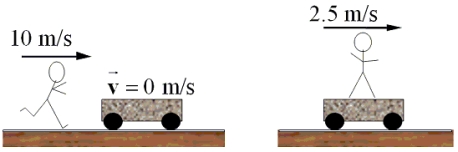
A) 150 kg
B) 175 kg
C) 210 kg
D) 260 kg
E) 300 kg
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During hockey practice, two pucks are sliding across the ice in the same direction. At one instant, a 0.18-kg puck is moving at 16 m/s while the other puck has a mass of 0.14 kg and a speed of 3.8 m/s. What is the velocity of the center of mass of the two pucks?
A) 5.0 m/s
B) 7.0 m/s
C) 9.0 m/s
D) 11 m/s
E) 13 m/s
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tennis ball has a velocity of 12 m/s downward just before it strikes the ground and bounces up with a velocity of 12 m/s upward. Which statement is true concerning this situation?
A) The momentum of the ball and the momentum of the earth both change.
B) Neither the momentum of the ball nor the momentum of the earth changes.
C) The momentum of the ball is changed; and the momentum of the earth is not changed.
D) The momentum of the ball is unchanged; and the momentum of the earth is changed.
E) Both the momentum and the kinetic energy of the ball change because of the collision.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 66
Related Exams