A) dispersion forces
B) dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds
C) dispersion forces and ion-dipole forces
D) dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
E) dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and ion-dipole forces
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrogen bonding is a special case of ________.
A) London-dispersion forces
B) ion-dipole attraction
C) dipole-dipole attractions
D) ion-ion interactions
E) none of the above
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 1 atm,an unknown sample melts at 49.9 °C and boils at 209.5 °C.If the temperature is 0°C,what is the state of matter for the sample?
A) solid and liquid in equilibrium
B) liquid
C) gas
D) solid
E) liquid and gas in equilibrium
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the ________ liquid crystalline phase,the component molecules exhibit ________ dimensional ordering.
A) nematic, one
B) smectic A, one
C) nematic, two
D) nematic, three
E) smectic B, one
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which molecule has hydrogen bonding as the predominant intermolecular force?
A) CH4
B) C6H6
C) CH3OH
D) CO2
E) C4H10
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On the phase diagram shown above,segment ________ corresponds to the conditions of temperature and pressure under which the solid and the gas of the substance are in equilibrium.
A) AB
B) AC
C) AD
D) CD
E) BC
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a phase diagram,the critical pressure is ________.
A) the pressure required to melt a solid
B) the pressure below which a substance is a solid at all temperatures
C) the pressure above which a substance is a liquid at all temperatures
D) the pressure at which a liquid changes to a gas
E) the pressure required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What intermolecular force is responsible for the fact that ice is less dense than liquid water?
A) London dispersion forces
B) dipole-dipole forces
C) ion-dipole forces
D) hydrogen bonding
E) ionic bonding
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phase diagram of a substance is shown above.The area labeled ________ indicates the solid phase for the substance.
A) w
B) x
C) y
D) z
E) y and z
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enthalpy change for converting 1.00 mol of ice at -25.0 °C to water at 50.0 °C is  The specific heats of ice,water,and steam are
The specific heats of ice,water,and steam are 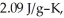
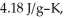 and
and 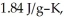 respectively.For
respectively.For 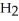 O,Δ
O,Δ 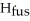 = 6.01 kJ/mol,and
= 6.01 kJ/mol,and 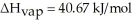 .
.
A) 12.28
B) 6.27
C) 10.71
D) 4709
E) 8.83
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has London dispersion forces as its only intermolecular force?
A) NBr3
B) CH3COOH
C) SiCl4
D) HBr
E) Cl2O
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
- 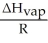 is the slope of a plot of the natural log of the vapor pressure of a substance versus ________.
is the slope of a plot of the natural log of the vapor pressure of a substance versus ________.
A) -1/T
B) -T
C) 1/T
D) T
E) 2T
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the enthalpy change (in kJ) associated with the conversion of 25.0 grams of ice at -4.00 °C to water vapor at 109.0 °C.The specific heats of ice,water,and steam are 2.09 J/g-K,4.18 J/g-K,and 1.84 J/g-K,respectively.For H2O,Δ 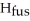 = 6.01 kJ/mol and Δ
= 6.01 kJ/mol and Δ 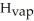 = 40.67 kJ/mol.
= 40.67 kJ/mol.
A) 64.8
B) 75.9
C) 11100
D) 12000
E) 112
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The property responsible for the "beading up" of water is ________.
A) density
B) viscosity
C) vapor pressure
D) surface tension
E) hydrogen bonding
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the predominant intramolecular force in NaNO3?
A) ionic bonding
B) ion-dipole attraction
C) dipole-dipole attraction
D) hydrogen bonding
E) London-dispersion forces
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following derivatives of methane has the highest boiling point?
A) CI4
B) CBr4
C) CCl4
D) CF4
E) CH4
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How high a liquid will rise up a narrow tube as a result of capillary action depends on ________.
A) the magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube, and gravity
B) gravity alone
C) only the magnitude of adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube
D) the viscosity of the liquid
E) only the magnitude of cohesive forces in the liquid
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which molecule is the least volatile?
A) CH3Cl
B) CH3I
C) CH3F
D) CH4
E) CH3Br
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phase diagram of a substance is given above.This substance is a ________ at 30 °C and 0.5 atm.
A) liquid
B) gas
C) solid
D) supercritical fluid
E) crystal
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The vapor pressure of any substance at its normal boiling point is ________.
A) 1 Pa
B) 1 torr
C) 1 atm
D) equal to atmospheric pressure
E) equal to the vapor pressure of water
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 124
Related Exams