A) oligopoly, monopolistic competition and perfect competition
B) perfect competition only
C) oligopoly and perfect competition
D) monopolistic competition and perfect competition
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A game in which pursuing dominant strategies results in noncooperation that leaves all parties worse off is a
A) prisoner's dilemma.
B) cooperative equilibrium.
C) first-price auction.
D) zero-sum game.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best explains why airlines often cut their ticket prices at the last-minute in order to fill the remaining empty seats on their flights?
A) Fixed costs in the airline industry are very large, but the marginal cost of flying one more passenger is very low.
B) Airlines receive a subsidy from the government for each flight that is fully booked and departs on time.
C) The Federal Aviation Administration ranks each airline based on the percentage of flights that are fully booked. These rankings affect the decisions of firms to use a particular airline to fly their employees to business meetings.
D) Cutting prices makes the airlines more popular with their customers, who may fly with the same airline in the future as the result of buying low-price tickets.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sequential game can be used to analyse whether a retail firm should build a large store or a small store in a city, when the correct choice depends on whether a competing firm will build a new store in the same city. Which of the following is used to analyse this type of decision?
A) a decision tree
B) a decision matrix
C) a sequential matrix
D) an either-or graph
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is important in determining the extent of competition in an industry?
A) the minimum level of short-run average total costs of production
B) the minimum efficient scale of production relative to market demand
C) whether or not the industry product is differentiated or standardised
D) the level of market demand for the industry's product
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists use game theory to analyse oligopolies because
A) real markets are too complicated to analyse without using games.
B) it is more enjoyable for economists and students to learn by playing games.
C) game theory helps us to understand why interactions among firms are crucial in determining profitable business strategies.
D) game theory is useful in understanding the actions of firms that are price takers.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal revenue for an oligopolist is
A) identical to the demand for the firm's product.
B) difficult to determine because the firm's demand curve is typically unknown.
C) downward sloping beneath the firm's demand curve.
D) horizontal on a price-quantity diagram.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The equilibrium in the prisoner's dilemma is a dominant strategy Nash equilibrium.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Competition in the form of advertising, better customer service, or longer warranties can also reduce profits by raising costs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
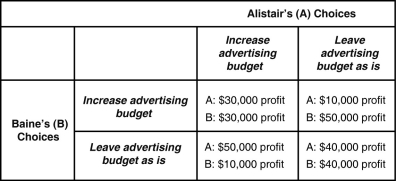 -Refer to Table 11-3. If Alistair assumes that Baine would increase its advertising budget, what should it do?
-Refer to Table 11-3. If Alistair assumes that Baine would increase its advertising budget, what should it do?
A) Alistair should keep its own budget the same and allow Baine to incur the higher cost.
B) Alistair should also increase its advertising spending.
C) Alistair should reduce its advertising spending.
D) Being a duopolist, Alistair is not affected by Baine's choices because it has a secure 50 per cent market share.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In economics, the study of the decisions of firms in industries where the profits of each firm depend on its interactions with other firms is called
A) decision theory.
B) game theory.
C) market structure analysis.
D) profit analysis.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not part of an oligopolist's business strategy?
A) deciding on how to manage relations with suppliers
B) choosing what new technologies to adopt
C) selecting which new markets to enter
D) independently setting a product's price without consideration of its rivals' pricing policies
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If one firm raises its price in an industry characterised by firms' facing kinked demand curves, it is likely that other firms in the industry will
A) reduce their prices to increase their market shares.
B) reduce their expenditure on advertising.
C) not change their prices.
D) increase their prices also.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of oligopoly?
A) the ability to influence price
B) a small number of firms
C) low barriers to entry
D) interdependent firms
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oligopoly differs from perfect competition and monopolistic competition in that
A) barriers to entry are lower in oligopoly industries than they are in perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive industries.
B) demand and marginal revenue curves are more useful for analysing oligopoly than they are for analysing perfect competition and monopolistic competition.
C) because oligopoly firms often react when other firms in their industry change their prices, it is difficult to know what the oligopolist's demand curve looks like.
D) the concentration ratios of oligopoly industries are lower than they are for perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive firms.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a second-price auction?
A) an auction in which the bidder who submitted the highest bid is awarded the object being sold and pays a price equal to the second highest amount bid
B) an auction in which the bidder who submitted the second highest bid is awarded the object being sold
C) an auction in which the bidder who submitted the highest bid is awarded the object being sold and pays a price equal to the average of the highest and second highest amount bid
D) an auction in which the bidder who submitted the second highest bid is awarded the object being sold and pays a price equal to the average of the highest and second highest amount bid
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A characteristic found only in oligopolies is
A) break even level of profits.
B) interdependence of firms.
C) independence of firms.
D) products that are slightly different.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the prisoner's dilemma is false?
A) The prisoner's dilemma in a one-shot game leads to a noncooperative, equilibrium outcome.
B) The prisoner's dilemma in repeated games could lead to cooperation, especially if there is some enforcement mechanism that punishes a player who does not cooperate.
C) Players caught in a prisoner's dilemma act in selfish ways that lead to an equilibrium that is sub-optimal.
D) The prisoner's dilemma game can never reach a Nash equilibrium as long as players do not cooperate.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider two oligopolistic industries selling the same product in different locations. In the first industry, firms always match price changes by any other firm in the industry. In the second industry, firms always ignore price changes by any other firm. Which of the following statements is true about these two industries, holding everything else constant?
A) Market prices are likely to be higher in the first industry, in which firms always match price changes by rival firms, than in the second, where firms ignore their rivals' price changes.
B) Market prices are likely to be lower in the first industry, where firms always match price changes by rival firms, than in the second, where firms ignore their rivals' price changes.
C) Market prices are likely to be the same in both markets because they are both oligopolistic markets.
D) No conclusions can be drawn about the pricing behaviour under these very different firm behaviours.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Collusion makes firms better off because if they act as a single entity (a cartel) , they can reduce output and increase their prices and profits. But some cartels have failed and others are unstable. Which of the following is a reason why cartels often break down?
A) Most cartels do not have a dominant strategy.
B) When a cartel is profitable, the amount of competition it faces increases.
C) Members of a cartel may resent having to share their profits equally.
D) Each member of a cartel has an incentive to 'cheat' on the collusive agreement by producing more than its share when everyone else sticks with the collusive agreement.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 186
Related Exams