A) Flow velocity
B) Discharge
C) Channel size
D) Maximum sediment grain size
E) None of these are correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of stream is shown in this photograph? 
A) Meandering stream
B) Braided stream
C) A stream whose main channel has high sinuosity
D) An esker
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would happen if the ice in this area melted away? 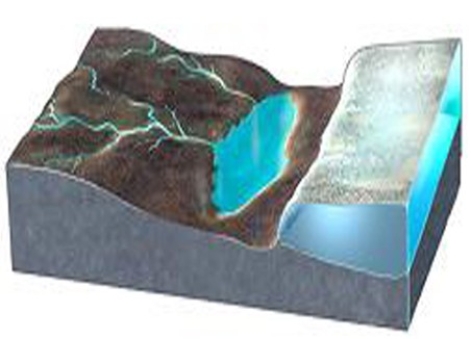
A) The land near the ice would drop due to isostatic rebound.
B) Rivers could change direction and flow away from the area once covered by ice.
C) The land subsides because the ice is removed.
D) All of these are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of feature shown in this figure is 
A) a braided stream.
B) river terraces.
C) alluvial fans.
D) entrenched meanders.
E) None of these are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following features are generally not associated with mountain streams and rivers?
A) Waterfalls
B) Rapids
C) Canyons incised into bedrock
D) Meanders
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can influence a stream's profile?
A) A rise in sea level
B) A fall in sea level
C) Tectonics
D) All of these are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following influences whether a flood occurs?
A) The height of levees
B) The amount of discharge
C) Urbanization (replacing farms or natural land with buildings)
D) The width of the channel
E) All of these are influences.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the features on this aerial photograph represents the former position of a meander? 
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Both C and D
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Feature A,formed where the Nile River encounters the Mediterranean Sea,is 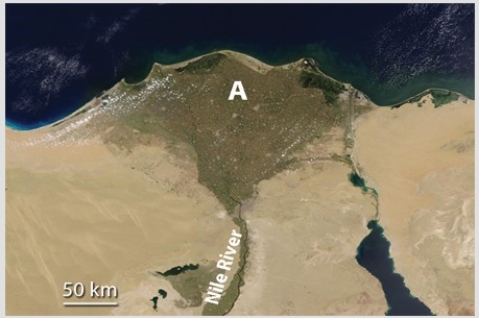
A) a landslide.
B) a series of waterfalls.
C) a delta.
D) All of these are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared with curve 2 on this hydrograph,what is a possible explanation for curve 1? 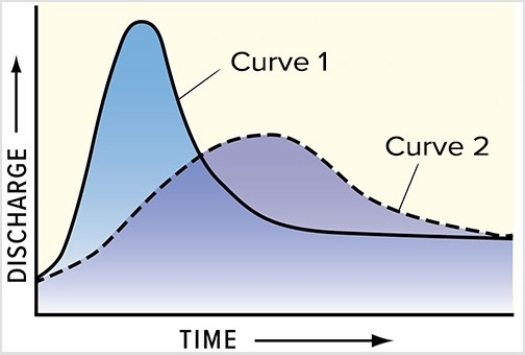
A) The basin for curve 1 has steeper slopes than the basin for curve 2.
B) The storm recorded by curve 1 was shorter and more intense than the storm represented by curve 2.
C) Curve 1 shows the same area as curve 2 but after urbanization.
D) All of these are possible.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pattern of discharge shown by this hydrograph? 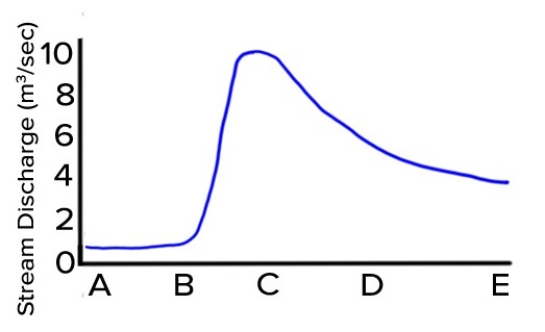
A) Discharge gradually increases and quickly decreases.
B) Discharge quickly increases and gradually decreases.
C) Discharge gradually decreases and quickly increases.
D) Discharges quickly decreases and gradually increases.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the main reason that a delta forms when a stream flows into a lake or sea?
A) The stream flows backward during high tide.
B) Ocean waves push the sediment up onto the beach.
C) The velocity of the stream decreases.
D) The stream began downcutting during the ice ages.
E) None of these are correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stream terraces represent
A) older floodplains of a river that has incised downward.
B) cutoff meanders of a meandering stream.
C) areas where sea level has risen and waves beveled across the coast.
D) None of these are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What was the cause of flooding in the 1993 upper Mississippi River flood?
A) Heavy snowmelt in Canada sent large volumes of water down the river in the spring.
B) A dam failed because it had been built in a risky place near a fault.
C) Persistent thunderstorms caused large amounts of rainfall over a several-state region.
D) Winter produced rain that melted snow that was on the ground.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which site along this stream would have the highest velocity for that segment of the stream? 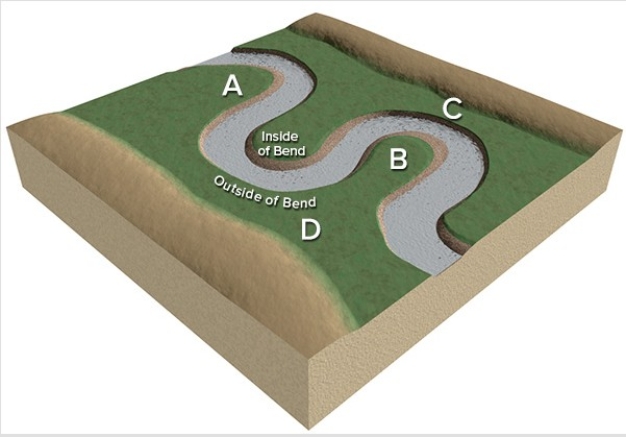
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparing these two curves on this hydrograph,the solid curve could record 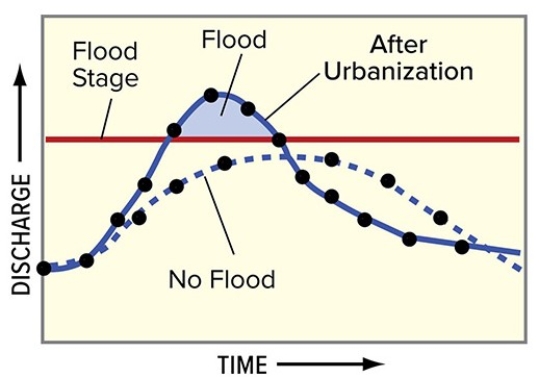
A) a shorter but more intense precipitation event.
B) the response of the stream to urbanization.
C) a more rapid spring snowmelt.
D) All of these are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where do mountain streams get most of their load of sediment?
A) Landslides,slope failures,and erosion of the mountain sides
B) Downward incision into bedrock
C) Abrasion of bedrock along the bottom of the channel
D) Alluvial fans
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does the associated graph indicate about a stream? 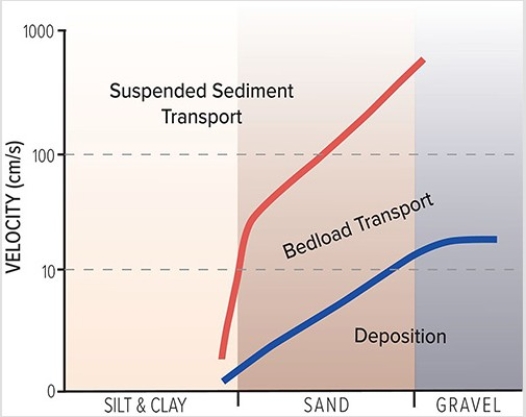
A) Silt and clay are carried in suspension under most stream velocities.
B) Sand and gravel are deposited at low velocities but transported at higher velocities.
C) Sand is carried in suspension only at high velocities.
D) As fast-moving water slows down,fine sand can switch from transport by suspension to the bed load.
E) All of these are correct.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 98 of 98
Related Exams